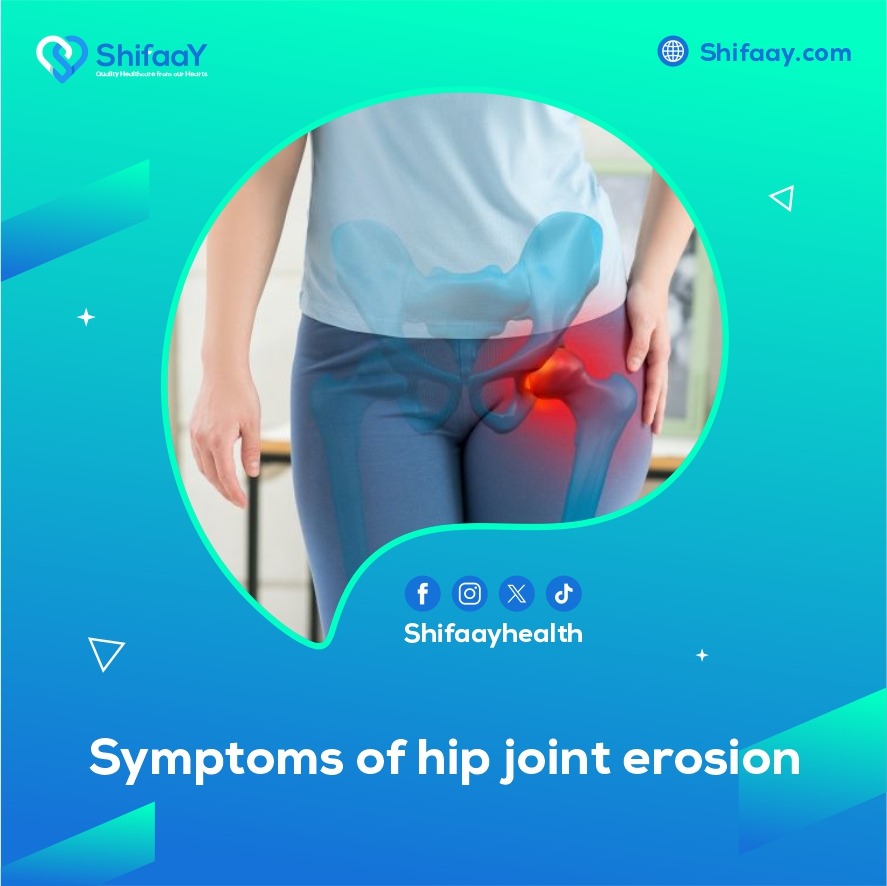
Symptoms of osteoarthritis of hip joint
Since the hip joint is one of the most important and active in the human body, many people, especially the elderly, constantly face significant challenges with joint health, particularly the hip joint. Many people experience symptoms of osteoarthritis of the hip joint, which is a growing health issue that affects many people’s lives. However, as we grow older, our bodies are more vulnerable to deterioration and corrosion. There are many reasons for this, but the most common ones are age, obesity, trauma to the hip area, genetic mutations, long-term illnesses, and so forth. All of these things can contribute to the development of osteoarthritis of the hip joint.
Early detection of the disease’s symptoms can be critical to maintaining mobility and quality of life. Conservative and non-surgical treatment options for early symptoms of osteoarthritis of the hip joint include exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding strenuous activities, taking painkillers, and using anti-inflammatory medications to reduce swelling and pain. Furthermore, osteoarthritis of the hip joint frequently manifests as persistent hip pain that can radiate to the knee or thigh and usually begins slowly before becoming worse with movement, making even simple daily tasks difficult.
Along with this terrible pain, people who have osteoarthritis of the hip joint may also have stiffness in the joint, especially after prolonged periods of sitting or rest. This stiffness can make it difficult for the person to move again. Note that this stiffness can occasionally be exacerbated by a sensation of friction or cracking in the joint when moving, which makes them feel even more uncomfortable. However, as the condition progresses, the affected person may encounter increasingly severe symptoms and encounter new challenges, such as losing their normal range of motion and finding it difficult to walk, bend, or even stand for extended periods of time. These developments may have a major impact on their ability to go about their daily lives and enjoy life as usual.
Timely and effective therapeutic approaches can greatly aid in the early diagnosis and selection of the best course of treatment, which may involve medication, physical therapy, or surgery in more severe cases, so the orthopedic doctors at Shifaay Center always advise seeking medical attention as soon as the symptoms of osteoarthritis of the hip joint arise. This article will cover the most prevalent signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis of the hip joint as well as how maintaining a healthy lifestyle and doing the appropriate exercise can either prevent hip osteoarthritis or minimize its negative effects.
osteoarthritis of the hip joint
As people age and participate in more daily activities, osteoarthritis of the hip joint becomes one of the health issues that significantly affects their quality of life. It is a common condition that causes a lot of chronic pain and difficulty moving from one place to another, which can make it difficult to understand. This condition, its causes, and treatment options are critical issues for both patients and healthcare providers. Notably, this condition is often caused by a number of different causes, including genetics, direct and repeated injuries, obesity, intense physical activity, excessive joint use, and so on. These factors can erode the cartilage covering the bones in the joint, causing the bones to rub against one another and eventually developing osteoarthritis of the hip joint, which is characterized by excruciating pain, swelling, and a restricted range of motion.
This can have a detrimental effect on the patients’ quality of life and everyday activities, even though many people with osteoarthritis of the hip joint may find it difficult to walk or climb stairs. However, it is important to note that there are currently many effective therapeutic approaches that can effectively treat osteoarthritis of the hip joint disease and relieve its symptoms in a safe and effective way. These therapeutic techniques can lessen pain and swelling while also strengthening the muscles that surround the joint and enhancing its range of motion. One of the most common types of treatment is non-surgical, which includes anti-inflammatory injections administered locally to reduce pain and swelling, physical therapy to enhance joint movement and quality of life, and pain management medications.
Additionally, patients with osteoarthritis of the hip joint may be able to replace their diseased joint with an artificial one through surgery as a form of treatment. This happens in severe symptoms of osteoarthritis of the hip joint where non-surgical treatment approaches have proven to be ineffective; in these situations, surgery is necessary. It is one of the most important factors that affects the ability to regain movement and effectively relieve pain. It is important to remember that osteoarthritis of the hip joint is a significant obstacle that can be easily overcome by implementing suitable treatment plans and working with specialized medical professionals to get the best outcomes. For this reason, the orthopedic doctors at Shifaay Center consistently advise maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in appropriate exercise, and avoiding activities that could exacerbate the condition.
Also follow: When does walking start after hip replacement?
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the hip joint
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint is common as people age and can have a significant impact on a patient’s quality of life, particularly for the elderly. This bothersome disease can limit daily activities and cause excruciating pain and mobility difficulties, so finding safe and effective treatment solutions is necessary to address this health issue.
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint can be treated with a range of innovative and effective therapeutic options, from simple procedures to surgical interventions. Notably, symptoms of osteoarthritis of the hip joint can be treated with non-surgical therapeutic approaches, such as changing lifestyles and losing weight to relieve pressure on the joints. Furthermore, performing exercises that strengthen the muscles surrounding the joint, as well as taking anti-inflammatory medications to relieve pain and swelling, including injecting steroids into the joint, can provide temporary relief from symptoms and pain.
Moreover, many may resort to surgery if conservative treatment methods fail; in this situation, it is the best option for getting rid of all pain and returning to a normal life.
Surgical options include joint restoration procedures or complete replacement with an artificial joint. Common surgical procedures such as pelvic joint replacements have been shown in studies to significantly enhance patients’ quality of life by enabling them to return pain-free to their regular activities after recovery. Even though it may take some time for a patient to fully recover from surgery, modern surgical methods have made the process safer and more efficient.
Furthermore, early diagnosis and treatment of symptoms of osteoarthritis of the hip joint may be essential for optimal outcomes and full recovery. This may necessitate close collaboration between the patient and our center’s medical staff, as this greatly aids in the development of a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to the patient’s needs and condition. Ultimately, this approach will undoubtedly result in a noticeable improvement in the patient’s condition and lessen the impact of osteoarthritis on his day-to-day activities.
Causes of osteoarthritis of the hip joint
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint is a prevalent and common health issue that affects a large number of people worldwide. It can also present significant challenges for both medical professionals and patients, as the condition consistently results in chronic pain and movement impairment. And below, we will discuss one of the main causes of osteoarthritis of the hip joint.
● Aging: It is commonly known that aging plays a significant role in the osteoarthritis of the hip joint because it can gradually reduce bone density, which makes the joint more vulnerable to damage.
● Genetic factors play an important and vital role in osteoporosis of the hip bones. If hip or bone disorders run in your family, you may be more susceptible to this problem.
● Genetic mutations that weaken and make the bone structure more fragile are one of the main causes of osteoarthritis of the hip joint, so it is essential to perform periodic examinations to detect early changes in bone density and take appropriate preventive measures.
● In addition to regular exercise, a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is necessary to maintain bone health. Inadequate nutrition and inactivity can exacerbate osteoarthritis of the hip joint, leading to weaker bones and an increased risk of fractures and erosion.
● Injuries and accidents are also one of the other main causes of osteoarthritis of the hip joint. Direct injuries to the hip, such as fractures or severe sprains, can damage the surrounding bone and cartilage. It is crucial to take all preventative measures to avoid injuries and preserve bone health because repeated injuries can also lead to cartilage osteoarthritis, which raises friction between the bones and causes corrosion.
Diagnosis of osteoporosis of the hip joint
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint is one of the most significant and famous painful conditions that is always in need of an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment to maintain quality of life. The progressive loss of cartilage covering the hip joint can cause the bones to rub against one another, causing severe pain and swelling, loss of movement, and difficulty moving from one place to another and back again. For this reason, it is essential to diagnose and treat the condition as soon as possible in order to avoid complications and improve therapeutic outcomes.
The diagnosis of hip osteoporosis usually begins with a comprehensive physical examination and a thorough medical history. The orthopedic specialist at the Shifaay Center, which is considered the best Center for Medical Tourism in Egypt, will identify the symptoms of osteoarthritis of the hip joint as well as the family’s medical history, any previous illnesses they may have had, and their daily routine, which may reveal during the physical examination that the patient has restricted range of motion in the joint and pain when moving. It should be noted that X-rays are the first step in the diagnosis process because they can display the space between the bones and the cartilage osteoarthritis. In certain situations, advanced imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans may be necessary due to their ability to yield more accurate data regarding the condition of surrounding tissues, cartilage, and bones.
Laboratory examinations and tests can greatly contribute to determining the presence of inflammation or infection, and the diagnosis of osteoarthritis of the hip joint may also involve a number of blood tests and examinations to rule out other diseases that may cause similar symptoms, such as rheumatoid arthritis or infection. We find that one of the most important factors in determining the extent of osteoarthritis and developing an appropriate treatment plan may be assessing the degree of pain and its impact on the patient’s daily functioning. If osteoarthritis of the hip joint is discovered early enough and treated appropriately, patients’ lives can be greatly improved and they can resume their daily activities without pain and with a higher quality of life.
Moreover, once osteoarthritis of the hip joint has been correctly diagnosed, it may be necessary to develop an effective treatment plan that takes the patient’s condition and degree of osteoarthritis into account. This is because different patients respond differently to different interventions. In cases of early disease, lifestyle modifications such as weight loss to lessen joint pressure, exercise to increase muscle strength and flexibility, and anti-inflammatory drugs to lessen pain and swelling may all be prescribed as treatments. In cases of advanced medical conditions, orthopedic surgery may be required to replace a hip joint.
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the femur head in children

Osteoarthritis of the femoral head in children is a common medical condition known as “Perthes disease.” It is a condition that affects the head of the femur in children. It results in inadequate blood flow to the bone, which can harm and erode the femur bones. Despite being an uncommon occurrence, parents may experience intense fear and anxiety due to the disease’s impact on their child’s mobility and day-to-day activities. Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the hip joint typically begin with pain in the thigh or knee, followed by lameness and difficulty moving.
Diagnosing “Perthes’ disease,” a osteoarthritis of the head of the femur in children, may require a number of precise tests, including X-rays and magnetic resonance imaging, depending on the extent of bone erosion. Treatment of this condition may depend on several important factors, most notably the age of the child and the stage of the disease. Conservative treatment in the early stages can include rest and physical therapy to strengthen the muscles surrounding the joint; children should be encouraged to avoid activities that increase thigh strain, such as running and jumping, and instead focus on activities that decrease joint strain, such as swimming and cycling.
However, in the event that the child is not responding to conservative treatment or if the disease progresses, early surgical intervention may be recommended. This will relieve all related pain and stop the disease from getting worse or developing complications, since in this case, surgery is essential to realign the femur’s head and improve blood flow to it. It is possible that these surgical procedures involve the use of orthotics and different methods of stabilizing the bone in order to improve joint stability. Keep in mind that a child will always need a “recovery period” after surgery, during which time intensive physical therapy may be required to gradually regain strength and movement.
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint in children is one of the major challenges that the child finds difficult to overcome easily; the best orthopedic doctors at Shifaay Center also advise giving the child the best medical care and psychological support during the course of treatment, as the family’s cooperation with the medical team and understanding of the child’s condition is crucial to the success of the treatment plan and the child’s ability to return to a normal life.
Is there a treatment for symptoms of osteoarthritis of the hip joint?
Yes, of course, as there are a variety of safe and effective therapeutic approaches that can help manage the symptoms of osteoarthritis of the hip joint. These approaches include biological treatment methods, anti-inflammatory drugs, physical therapy, local injections of cortisone, and surgery, such as replacement hip joint surgery, which is required in extreme cases of illness. It should be noted that the best treatment option always depends on the severity of the osteoarthritis and the general condition of the patient.
Can osteoarthritis of the hip joint be cured?
Yes, of course, but fully recovering from hip arthritis can be a difficult challenge. However, with the help of readily available and efficient therapeutic approaches, symptoms of osteoarthritis of the hip joint can be managed and quality of life enhanced. These approaches may include anti-inflammatory drugs, physical therapy, weight loss, appropriate exercise, and, in extreme situations, surgical intervention—which is the most effective way to reduce pain and enhance mobility.
How long does hip joint treatment take?
The duration of treatment for symptoms of osteoarthritis of the hip joint may vary from each patient to another, as it depends on several factors, including the severity of the condition and the type of treatment used, whether it is medication or conservative treatment, such as physical therapy, which may take from several weeks to several months to achieve amazing and effective results, but if the patient resorts to surgical intervention such as hip replacement, full recovery may take from three to six months after surgery.