Symptoms of Venous Insufficiency in the Legs
In a world filled with numerous chronic diseases, chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) stands out as one of the more serious yet often underestimated conditions. Many individuals tend to dismiss the early signs, although it can significantly impact the patient’s quality of life if left undiagnosed and untreated. In its initial stages, symptoms may seem mild—such as a feeling of heaviness in the legs or slight swelling after prolonged standing—which leads many to ignore them or attribute them to simple fatigue. However, the issue is far more complex. These symptoms may indicate an early circulatory disorder known as chronic venous insufficiency, typically caused by weakened or damaged venous valves. When these valves fail to function properly, blood flow back to the heart becomes inefficient, leading to pooling of blood in the lower extremities and the gradual onset of symptoms that can worsen over time without proper medical intervention.
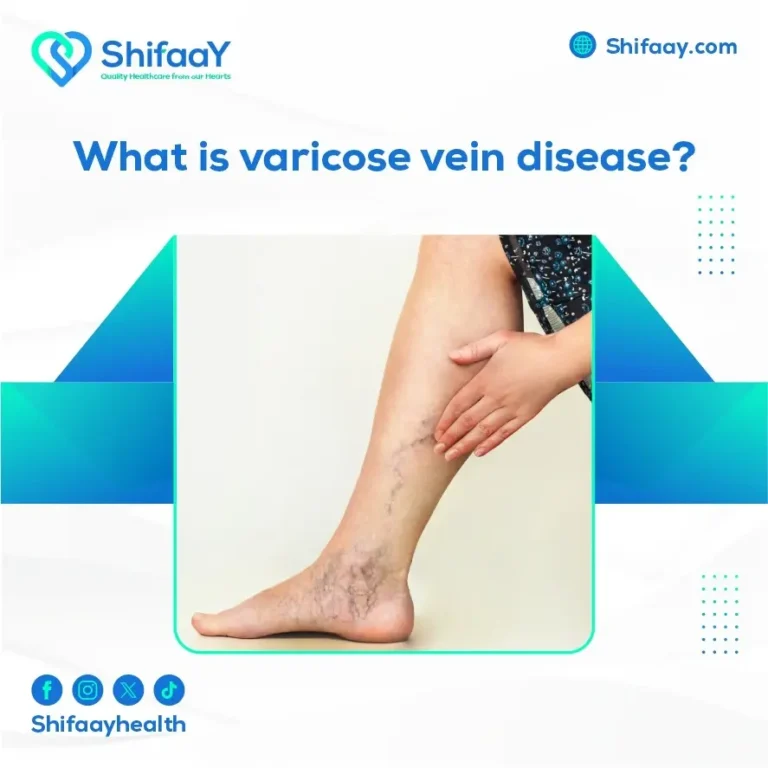
Chronic venous insufficiency is a common vascular condition that primarily affects the veins, especially in the legs. It occurs when the valves inside the veins fail to work effectively, causing blood to flow backward instead of upwards toward the heart. This leads to blood accumulation in both the superficial and deep veins, along with a rise in venous pressure—medically known as chronic venous hypertension. The constant elevation in pressure causes the veins to stretch and lose their elasticity over time, which exacerbates symptoms and makes them more prominent and distressing.
Key symptoms include persistent leg heaviness and fatigue, continuous swelling (particularly around the ankles), and chronic pain that worsens with prolonged standing or sitting. Visible varicose veins may also appear beneath the skin. Additionally, some patients may experience changes in skin color—typically dark brown or bluish—along with dry, itchy skin.
Neglecting treatment for chronic venous insufficiency can result in serious health complications that may interfere with the ability to carry out normal daily activities. Therefore, seeking care from specialized medical centers, such as Shifaay Healthcare Center, represents a vital step toward effective management. This center provides precise evaluations using the latest medical imaging technologies, along with personalized treatment plans that may include compression stockings, pharmacological therapy, and non-surgical interventions like laser therapy or sclerotherapy. Moreover, the center emphasizes continuous patient follow-up and guidance to prevent symptom recurrence or progression. Early intervention offers a real opportunity to restore quality of life and protect long-term leg health.
Causes and Risk Factors of Chronic Venous Insufficiency
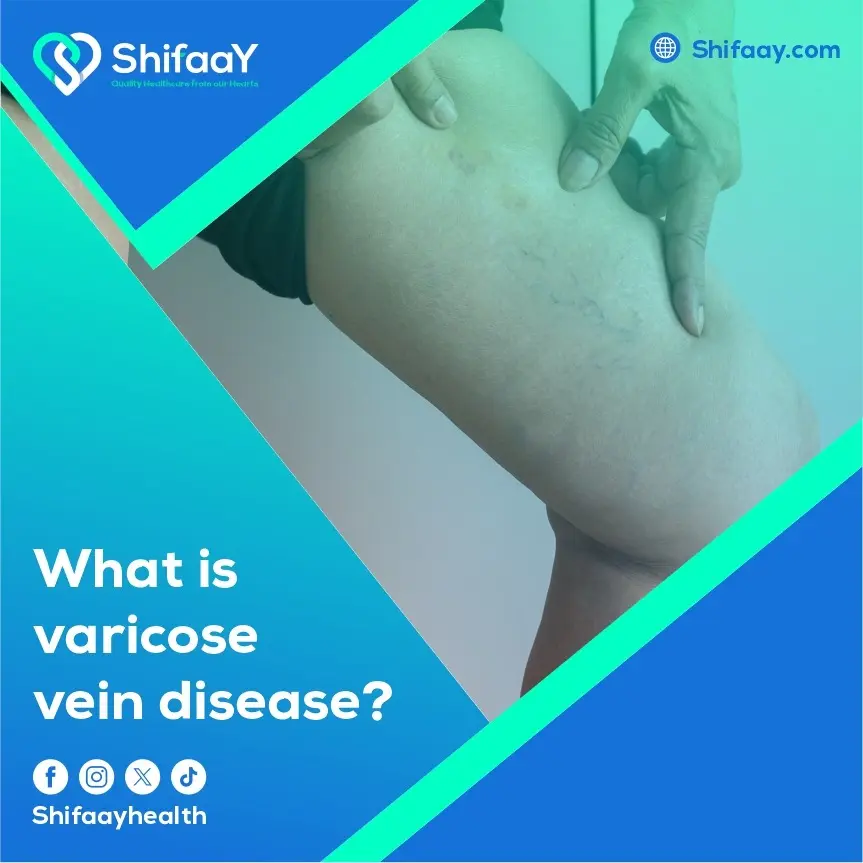
It is important to understand that chronic venous insufficiency is a widespread medical condition that may appear minor at first, but it often conceals significant physical and emotional suffering if not addressed in time. Over time, symptoms may gradually worsen—from a mere sensation of heaviness or fatigue in the legs to chronic pain, persistent swelling, skin discoloration, and even ulcers that are difficult to heal. This is what makes CVI a serious condition—not just because of its physical toll, but also its emotional and psychological impact on daily life.
Recognizing the underlying causes and being aware of risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing CVI is essential for anyone seeking to safeguard their health and prevent this often-silent disorder from becoming a constant source of distress.
Main causes of chronic venous insufficiency include:
- Weak or damaged venous valves that normally prevent blood from flowing backward.
- Previous deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which may compromise vein function.
- Weak leg muscles that reduce the efficiency of blood pumping toward the heart.
- Genetic factors that predispose some individuals more than others.
- Risk factors that may increase the chance of developing this condition include:
- Prolonged standing or sitting, common in office jobs or certain professions.
- Aging, as vein walls gradually weaken with time.
- Obesity, which adds excess pressure on the veins.
- Pregnancy, due to increased blood volume, hormonal changes, and pressure on pelvic veins.
- Smoking, which weakens blood vessels and impairs circulation.
Read aslo: Carotid Endarterectomy (CEA)
Diagnosing Chronic Venous Insufficiency: Tests and Procedures
Diagnosing chronic venous insufficiency is the first and most crucial step toward effective treatment and restoring quality of life. Diagnosis aims not only to determine the severity of the condition but also to uncover underlying causes and identify potential complications that may silently develop over time.
Many patients suffer from symptoms such as leg heaviness, swelling, nighttime cramps, or skin discoloration for extended periods without realizing these signs may indicate venous valve dysfunction and blood pooling in the lower limbs. This highlights the importance of early diagnosis as a cornerstone in preventing more severe complications, such as venous ulcers or thrombotic events.
Initially, a specialist will conduct a thorough medical history review, discussing all symptoms in detail—such as heaviness, swelling, pain, or skin color changes—while also assessing for hereditary factors or lifestyle patterns that could contribute to the condition.
This is followed by a clinical examination, during which the doctor will inspect the legs for visible swelling, varicose veins, or skin changes that suggest impaired venous circulation.
Among the most important diagnostic tests is the Doppler ultrasound, which is considered one of the most accurate tools for evaluating venous valve function, blood flow speed, and detecting any blockages or venous reflux.
In some cases, a venous stress test or comprehensive duplex scan—which combines ultrasound with color imaging—may be performed to precisely assess the extent of the damage.
Diagnosis also takes into account several key factors such as age, gender, obesity, work habits, and the presence of chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension, in addition to family history of varicose veins or thrombosis.
The goal of diagnosing chronic venous insufficiency is not only to identify the root cause of the condition but also to design a targeted and effective treatment strategy. This is the area of expertise at Shifaay Healthcare Center, which is committed to offering a complete medical experience that begins with attentive care and continues through evidence-based solutions and personalized support.
Treatment of Chronic Venous Insufficiency with Compression Stockings
There are numerous treatment options available for chronic venous insufficiency (CVI), typically depending on the underlying causes and the stage of the condition. One of the most common and effective conservative treatments is the use of compression stockings. These stockings, made of elastic and stretchable materials, apply graduated pressure to the legs—starting at the ankle and gradually decreasing up to below the knee or thigh. This mechanism greatly enhances blood flow in the lower limb veins and helps reduce swelling caused by blood pooling in the extremities. This method is considered a first-line conservative therapy, particularly recommended in the early stages of the disease.
Compression stockings used for treating chronic venous insufficiency are available in various sizes and pressure levels. The appropriate type is selected based on a physician’s diagnosis, who determines the exact level of compression required for each patient. In certain cases, such as in the presence of ulcers or non-healing skin wounds, specialized dressings may be used, such as the “Unna boot”—a multilayered medical bandage tightly wrapped around the leg and foot to reduce swelling and promote skin healing.
In addition to local treatment, patients are often advised to adopt specific lifestyle modifications that effectively alleviate symptoms. These include elevating the legs while lying down to improve blood return to the heart and engaging in regular walking to stimulate circulation. Furthermore, weight loss plays a critical role in reducing pressure on the veins, especially for obese individuals.
In some cases—particularly when chronic venous insufficiency is linked to a history of deep vein thrombosis—doctors may prescribe anticoagulants (commonly referred to as blood thinners). These medications help dissolve existing clots and reduce the risk of new clot formation.
Regular follow-up with a specialized medical team, such as the professionals at Shifaay Healthcare Center, ensures that patients receive a comprehensive treatment plan that integrates pharmacological, behavioral, and advanced medical approaches to manage the condition and enhance quality of life.
Read aslo: best teeth whitening methods
Complications of Chronic Venous Insufficiency
Chronic venous insufficiency is a common medical issue that can significantly affect quality of life if not treated promptly. While it may start with mild symptoms such as leg heaviness or slight swelling, it can progress to a range of complex complications that may impair mobility and daily activities. This highlights the importance of early detection and timely medical assessment, as neglecting the condition can lead to worsening symptoms and increase the risk of serious health consequences.
In our commitment to raise awareness and provide valuable health information, we emphasize the following potential complications of chronic venous insufficiency if left untreated or mismanaged:
- Venous Leg Ulcers: Among the most common and serious complications, these painful ulcers typically form around the ankle and are difficult to heal without specialized medical care.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Chronic venous insufficiency often paves the way for blood clots to develop in deep veins, posing a serious risk of pulmonary embolism if clots travel to the lungs.
- Persistent Leg Swelling: Caused by impaired venous return, this chronic fluid retention can make walking difficult and make it hard to wear shoes.
- Skin Discoloration and Hardening: The skin may turn dark brown and become thickened and stiff, indicating disease progression and worsening circulation.
- Venous Eczema: A chronic rash that may develop into skin infections requiring long-term treatment.
- Persistent Pain or Itching: These symptoms can significantly affect sleep and overall comfort.
Preventing Chronic Venous Insufficiency: Daily Tips
Did you know that leg heaviness or swelling at the end of the day may be your body’s first warning sign of poor blood circulation? This is not something to ignore, as it often signals the onset of chronic venous insufficiency—a common condition that starts mildly but may worsen over time and affect your mobility and lifestyle. As the venous valves weaken, blood flow from the legs to the heart becomes more difficult, leading to blood pooling and increased venous pressure. The good news is that this condition can be prevented in its early stages by following some simple daily preventive measures:
- Stay active throughout the day. Even if you have a sedentary job, stand up and move around for a few minutes every hour to promote blood flow.
- Elevate your legs when lying down or sitting for long periods. This reduces venous pressure and improves circulation.
- Avoid tight clothing, especially around the thighs and legs, as it can restrict blood flow.
- Engage in light exercise such as walking or swimming regularly. These activities are particularly beneficial for venous health.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce pressure on your leg veins. Follow a diet rich in fiber and vitamins while reducing salt intake to avoid fluid retention.
- Drink enough water daily to maintain healthy blood viscosity and reduce clotting risks. It’s also crucial to quit smoking, as it adversely affects vascular health.
- Wear medical compression stockings if needed, especially during long standing periods—but always consult your doctor beforehand.
When Should You See a Doctor for Symptoms of Chronic Venous Insufficiency?
If you’re experiencing unusual heaviness in your legs, swelling that worsens by the end of the day, or notice bulging, rope-like blue veins on your skin, these may be clear indicators of early chronic venous insufficiency. This condition should not be overlooked, as it may require timely medical intervention. Many people dismiss such symptoms as mere fatigue or the result of prolonged standing, unaware that neglecting them can lead to more serious issues such as chronic skin ulcers or venous thrombosis.
Below are some warning signs that should prompt you to visit Shifaay Healthcare Center immediately:
- Persistent swelling in the legs or ankles for several days without improvement.
- A burning sensation, itching, or chronic numbness in the legs that interferes with comfort.
- Discoloration of the skin, especially if it becomes dark brown.
- Development of ulcers or wounds—particularly around the ankles—that are slow to heal.
- Severe pain while standing that improves when legs are elevated.
- Noticeably enlarged, painful, or swollen veins.
Surgical Treatments for Chronic Venous Insufficiency: When Are They Necessary?
Surgical treatments for chronic venous insufficiency represent one of the effective therapeutic options for patients suffering from persistent complications that do not respond to conservative management. But when does surgery become a necessary step? Is it essential to resort to surgery immediately after diagnosis? Or are there specific indicators that help determine the right timing for surgical intervention? These are common questions that many patients face—especially those who experience daily pain, bothersome swelling, and noticeable skin changes due to poor venous circulation in the lower limbs.
To begin with, it is important to understand that chronic venous insufficiency is not merely a cosmetic issue, as many people believe. Rather, it can evolve into a persistent condition that significantly affects the patient’s quality of life and may lead to serious complications such as venous ulcers or thrombosis. When non-surgical treatments—such as compression stockings, lifestyle modifications, or pharmacologic therapy—fail to produce tangible improvement, it becomes necessary to consider surgical options as a critical therapeutic step aimed at improving blood flow in the affected veins and restoring functional comfort for the patient. Surgery should never be seen as a quick fix or arbitrary choice; it is the outcome of a thorough medical evaluation that takes into account the severity of symptoms, progression of the condition, and the presence of complications such as bleeding or non-healing ulcers.
At this point, patients often begin to ask: Do I really need surgery, or can I wait? Will I feel immediate relief after the operation? What are the available treatment options? Is there a significant difference between laser, radiofrequency, and traditional vein stripping? The answers to these questions rely entirely on accurate diagnosis using imaging tools such as venous Doppler ultrasound and close monitoring of symptom progression over time. Thus, the physician plays a key role in guiding the patient toward the appropriate treatment decision based on clinical evidence rather than temporary discomfort or superficial symptoms.
The Difference Between Chronic Venous Insufficiency and Varicose Veins
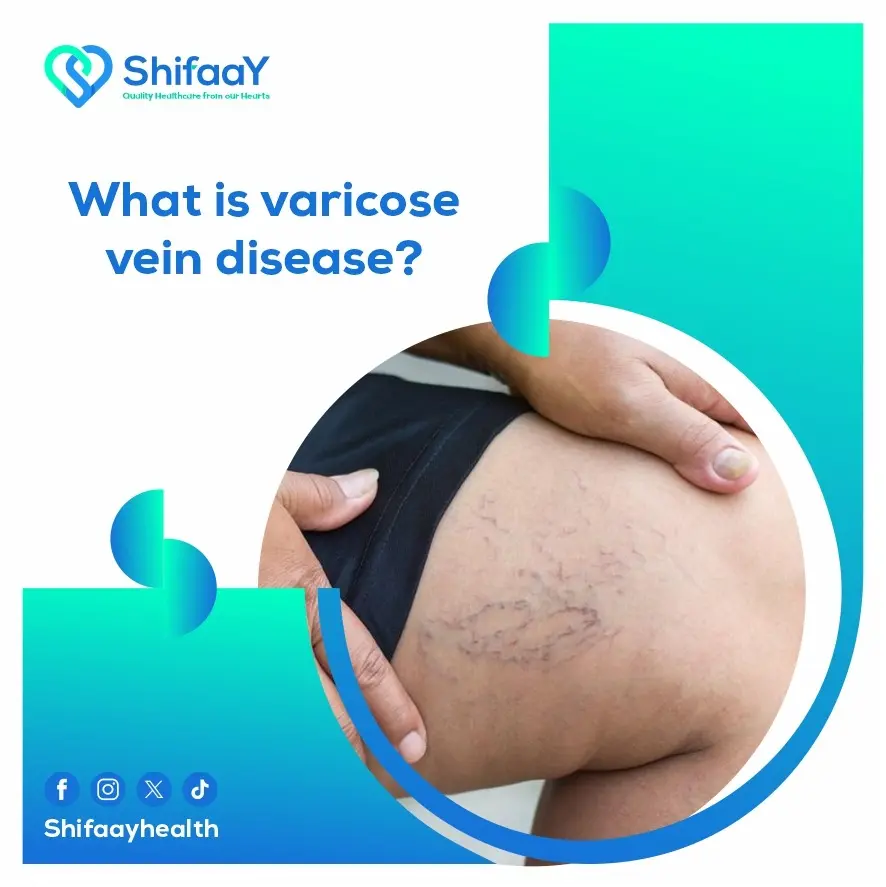
Undoubtedly, both chronic venous insufficiency and varicose veins are among the most common vascular disorders, particularly affecting the legs and having a direct impact on an individual’s quality of life—especially when left untreated or improperly managed. Despite their prevalence, many people tend to confuse the two conditions and mistakenly believe they are the same. This misunderstanding often leads to delayed diagnosis and, consequently, delayed treatment. So, what is the real difference between chronic venous insufficiency and varicose veins? And how can their symptoms be distinguished? In this section, we will clarify the main differences in a simplified and practical way by focusing on their causes, symptoms, and potential complications—highlighting the importance of early diagnosis and medical follow-up. This aims to empower the reader to differentiate between the two and take the right action at the appropriate time to preserve their health and quality of life.
First: Chronic Venous Insufficiency
This is a common medical condition that usually results from malfunctioning valves in the deep veins of the legs, causing blood to pool in the lower extremities instead of returning to the heart. Key symptoms of this condition include ankle swelling, leg heaviness and pain, itching, skin discoloration, and—in advanced cases—chronic skin ulcers.
Chronic venous insufficiency is considered one of the most progressive vascular disorders, often affecting individuals who stand or sit for long periods, those who are obese, or people with limited mobility. It typically requires early diagnosis and regular treatment to prevent complications. Treatment options include compression stockings, physical activity, and sometimes medical or surgical interventions.
Second: Varicose Veins
Varicose veins are enlarged, twisted superficial veins that typically appear beneath the skin as a result of weakness in the vein walls or valve dysfunction, leading to blood pooling in these veins. They are usually visible to the naked eye and most commonly affect the legs.
Symptoms of varicose veins include mild pain, leg heaviness, burning sensation, and nighttime cramps, which often worsen after prolonged standing. Although varicose veins may initially appear to be a cosmetic concern, they can progress and lead to inflammation or bleeding if left untreated. Effective treatment options for varicose veins include laser therapy, sclerotherapy (injections), or minor surgical procedures.
The fundamental difference between the two conditions is that chronic venous insufficiency affects the deep veins and is generally more complex, whereas varicose veins are a superficial issue that is often visible externally.
What is the difference between varicose veins and chronic venous insufficiency?
Varicose veins are enlarged and twisted superficial veins that typically appear in the legs due to valve dysfunction, while chronic venous insufficiency is a broader disorder involving impaired venous return and blood pooling in the legs due to chronic valve failure.
Can chronic venous insufficiency be completely cured?
Chronic venous insufficiency cannot always be completely cured, but it can be effectively managed through conservative or surgical treatments that aim to reduce symptoms and prevent complications—especially when diagnosed and treated early.
What are the complications of untreated chronic venous insufficiency?
Neglecting treatment for chronic venous insufficiency may lead to complications such as chronic swelling, skin ulcers, skin discoloration, phlebitis, or even serious blood clots, all of which can severely affect mobility and overall quality of life.