Anterior cruciate ligament tear and treatment
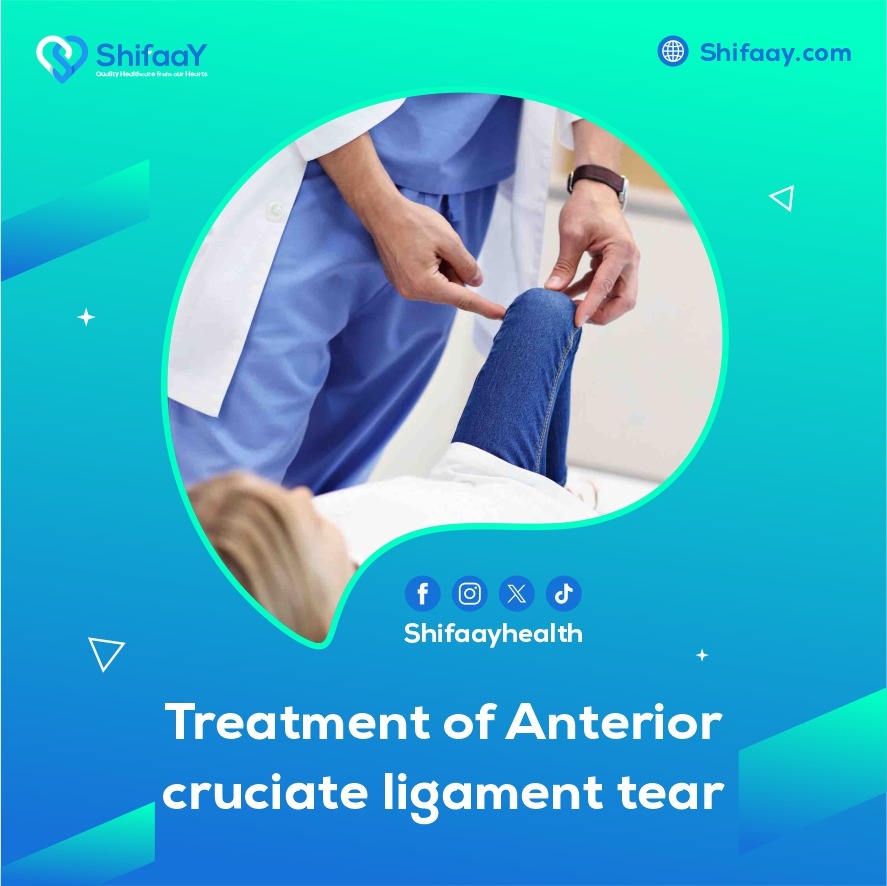
Treatment of anterior cruciate ligament tear, Anterior cruciate ligament tears are among the most common, complicated injuries that impair people’s ability to perform and lead normal lives. As such, many people, particularly athletes, are constantly searching for anterior cruciate ligament tear and treatment. This common pathological condition affects the knee joint and is usually caused by exposure to one of the injuries from sports or violent accidents. Effective therapy aimed at restoring knee function and lowering the risk of developing future issues is required for the treatment of this condition.
Anterior cruciate ligament tears are treated with analgesic medications and ice packs to minimize pain and swelling. After that, clinical examinations and medical imaging are used to carefully assess the extent of the injury and its impact on the strength and stability of the knee. However, in cases of severe injury, a thorough and effective surgical intervention may be considered necessary. It is critical to regain the self-assurance and safety necessary to participate in sports activities because the ultimate goal is to fully restore the joint’s range of motion and stability, minimize complications and side effects, improve treatment results, and strengthen the surrounding muscles, which may aid in pain relief and stability.
Restoring the knee’s natural range of motion, lowering the chance of further issues, and ensuring a full, sustainable recovery are all dependent on the patient following certain guidelines for physical therapy sessions and at-home exercises. These guidelines are provided by the best orthopedic surgeon at Shifaay Center , which is regarded as the best medical tourism center in Egypt.
Treatment of posterior cruciate ligament partial tear
Treating a posterior cruciate ligament partial tear requires immediate attention and intense care. Applying ice and taking painkillers may be the first line of treatment, which aims to reduce inflammation and relieve pain. After determining the extent of the injury, the optimal course of treatment is selected. In some simple cases, physical therapy might be all that is needed to rebuild the surrounding muscles of the knee in terms of strength and mobility. But in more complicated and severe cases, the condition might necessitate immediate surgical intervention to treat the posterior cruciate ligament partial tear, along with strict adherence to a post-operative treatment and rehabilitation program to ensure full knee function and reduce the risk of recurrence.
It is crucial to keep in mind that the primary factors that may affect how the posterior cruciate ligament partial tear is treated are the severity of the injury and how it affects the patient’s quality of life and level of activity. This therapy could involve both surgery and non-surgery. Below, we will explain to you some possible treatment options:
● Physical therapy can be one of the effective treatment options used to improve the strength and stability of the muscles surrounding the knee.
● Exercises aimed at building muscle can support and stabilize the injured knee.
● If the injury is severe or non-surgical treatment is not working, surgery might be the best course of action for treating the posterior cruciate ligament partial tear.
Follow also: Treatment of knee articular cartilage tear
Treatment of anterior cruciate ligament tear
Anterior cruciate ligament tear is among the most frequent and extensive injuries to which the knee may be vulnerable; prompt treatment is necessary to restore knee function and reduce the risk of complications and side effects. Analgesic medications and ice application to the injured area are the first lines of treatment of anterior cruciate ligament tear. It should be noted that x-ray imaging and laboratory testing are utilized to evaluate the degree of injury and the knee joint’s apparent stability. In addition, physical therapy may include strengthening the muscles surrounding the knee as well as improving stability and balance.
In cases of severe anterior cruciate ligament tear or those requiring intense sporting activity, surgery may be very necessary and important as it always aims to stabilize the torn part and completely treatment of anterior cruciate ligament tear, which could help restore function to the knee and lower the risk of further injury. The major objectives of physical therapy sessions that may be a part of the post-operative rehabilitation process are the restoration of knee strength, stability, and mobility.
Anterior cruciate ligament tear symptoms
Numerous people may experience a range of significant common symptoms, from moderate to severe and agonizing, depending on a number of factors, most notably the severity of the injury and the difference in medical conditions. Some of the most notable of these symptoms are as follows:
● Knee pain:
Sometimes the patient may feel some severe pain in the knee, especially when trying to put weight on it or during a sporting activity.
● Knee swelling:
The knee joint may become visibly swollen as a result of some inflammation and irritation resulting from this injury.
● Instability:
Patients often experience a sensation of instability in the knee, particularly when standing on one foot or executing certain movements that call for stability.
● Knocking sound:
A common symptom of a potential cruciate ligament tear and rupture is hearing a cracking sound, which could come from the knee joint.
● Weakness in surrounding muscles:
The patient may notice noticeable weakness in the muscles near the knee joint, which may greatly affect the ability to carry out daily activities normally.
● Swelling and bruising:
It is possible for an anterior cruciate ligament tear to be accompanied by noticeable swelling and bruising in the knee region.
If you have any of these symptoms and think you may have an anterior cruciate ligament tear, you should see a specialist orthopedic doctor at Shifaay Center. They will evaluate your condition, conduct a precise examination, and make the diagnosis. Based on their findings, you can begin the appropriate course of treatment, which may include surgery or non-surgical measures, to minimize complications and hasten the healing process.
Causes of anterior cruciate ligament tear
The anterior cruciate ligament tear is a frequently occurring and extensively distributed injury that can affect a large number of individuals for any of the following reasons:
● Sports injuries:
Playing sports like football, basketball, and ski ball that require quick changes in direction, high jumps, and a lot of strain on the knee, is one of the main things that can cause an anterior cruciate ligament tear.
● Accidental injuries:
Anterior cruciate ligament tear can result from being involved in an accident, such as one of the most costly car accidents or a serious fall that injures the knee.
● Excess tensions:
An anterior cruciate ligament tear can occur from subjecting the knee to excessive strain or from carrying heavy objects that may be too much for the knee to support.
● Genetic factors:
Anterior cruciate ligament tearsl can occur more frequently in people with high legs, structural knee deformities, and other genetic factors.
● Other factors:
Anterior cruciate ligament tear may also result from a number of other significant factors, including psychological stress, inadequate physical fitness, imbalanced muscles, and improper training.
It is important to stress that being aware of these important variables can assist in taking the appropriate safety measures, such as maintaining a high level of physical fitness and strengthening the knee muscles, to reduce the risk of the anterior cruciate ligament tear.
The difference between a cruciate ligament tear and rupture

Although the terms “tear” and “rupture” refer to similar cases of damage to the cruciate ligament in the knee joint, there may be some important distinctions between the two. Understanding these distinctions may be essential for a proper examination, diagnosis, and course of treatment. The most prominent of which are the following:
● First, the cruciate ligament tear:
Which means the anterior cruciate ligament is partially or completely torn. This rupture occurs when the cruciate ligament is subjected to excessive stress or force, which causes the ligament fibers to separate from one another. It is important to note that the tear can be partial or complete, and the severity can vary. Dealing with them must be done according to the severity of the tear.
● Secondly, the cruciate ligament rupture:
Cruciate ligament rupture is a condition of partial damage to the cruciate ligament fibers without complete separation. This condition can be caused by an acute or repetitive injury, resulting in a torn cruciate ligament that is not completely severed.
Differences between tearing and rupture:
● Severity of injury:
The anterior cruciate ligament tear is considered more serious than a rupture, as the ligament separates completely or partially.
● Diagnosis:
A cruciate ligament tear is easier to diagnose than a rupture because the ligament is clearly separated.
● treatment:
Typically, a cruciate ligament tear may require surgical treatment to repair it, while a cruciate ligament rupture can be treated through rehabilitative exercises or physical therapy.
It is important to note that understanding the distinction between rupture and cruciate ligament tears can help you choose the best course of action for your specific condition and better direct the therapeutic approach to facilitate the desired recovery and restore function to your knee.
Treatment of anterior cruciate ligament tear without surgery
Individuals with anterior cruciate ligament tear could be concerned that surgery is the best course of action for their injury. However, surgery may not always be necessary to treat the condition, particularly if the tear is small and incomplete. If there are no concomitant conditions, rehabilitation and physical therapy are among the best options for treating anterior cruciate ligament tear; these may entail a few intense sessions with a specialized physical therapy doctor who uses strengthening and stretching exercises to improve balance and stability as well as strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee. It should be noted that the rehabilitation program’s design may incorporate pain management and knee function restoration, contingent upon each patient’s unique condition.
The most common form of treatment of cruciate ligament tear is a splint, which serves to support and relieve pressure on the injured ligament while it heals. Other treatments include physical therapy and more time-consuming procedures like applying ice and painkillers to reduce swelling and pain. The patient must consider one of the surgical treatment options if no improvement has been observed.
Also follow: The best physical therapy center in Egypt
Is it possible to live with an anterior cruciate ligament tear?
It is possible to live with an anterior cruciate ligament tear, provided that the tears heal over time. The treatment plan that the specialist surgeon recommends must be followed in order to reduce pain, minimize complications and side effects, and decrease the likelihood of recurrence.
How long does it take to heal an anterior cruciate ligament?
Depending on how severe the injury is, recovery from an anterior cruciate ligament injury can take anywhere from 2-4 weeks to 10–12 weeks. However, in general, some patients can walk without assistance after surgery, albeit only for short distances. With physical therapy sessions, the patient can fully recover in as little as six to twelve months, and he can run and walk more quickly in as little as one week.
Is it possible to repair the cruciate ligament without surgery?
Of course, but in many affected medical cases—such as athletes—that always require movement and activity, anterior cruciate ligament surgery may play a significant and highly beneficial role. This is because the anterior cruciate ligament tear cannot heal without surgical intervention, in which case the surgeon repairs the anterior cruciate ligament and its remodeling.